|
 |
 |
Manure
Management System
| Solid Manure Being Loaded into
Spreader |

|
| Solid Manure Ready for Transport
to the Field for Application |
 |
Beef cattle manure can be handled as a solid, semi-solid or a liquid.
The bedding used in loafing sheds will form a manure pack with the manure
incorporated into the bedding material. Common bedding materials include,
straw, sand, wood shaving, sawdust, recycled newspaper print, and chopped
corn stalks. Generally, the manure pack is removed once or twice a year
and spread onto cropland or pastureland for use as a fertilizer resource.
Solid manure scraped from open lots is usually applied to cropland after
removal, or stockpiled in a solid manure storage facility near the feedlot.
Solid manure storage is generally in a structure with a paved floor and
walls on three sides to allow the material to be stacked. In humid areas,
manure storages may need to be covered to keep the manure drier. Solid
manure is surface applied to cropland with a box-type manure spreader
or a flail-type manure spreader. Clean up-slope runoff water and roof
water should be diverted around the manure storage to minimize the amount
of storage needed.
| Solid Manure Being Surface Applied
with Box Spreader |

|
| Solid Manure Being Field Applied
with Side Slinging Spreader |
 |
Manure in a liquid or semi-solid form (slurry) is generally stored for
at least 180 days before removal and application to cropland or pastureland.
Depending on the site, pumps, transfer pipes or channels may be required
to move the manure from the animal housing areas to storage. Semi-solid
manure is stored in either above ground concrete or steel tanks or below
ground earthen or concrete tanks. Liquid manure may be stored in formed
tanks, earthen storages, or in earthen lagoons
that can consist of one cell or more cells. Lagoons provide treatment
of the manure (by anaerobic, aerobic
or a combination of aerobic and anaerobic processes) as well as storage.
Composting is another option for solid manure management.
| Shed and Outside Lot with Runoff
Control |
 |
| Manure Scraped to Sump and Stored
as a Slurry |
 |
Runoff from open cattle lots must be controlled, especially during heavy
rainfall events. Runoff control systems include settling basins (to remove
manure solids) in combination with earthen detention ponds; transfer of
runoff into a lagoon system; or for small feedlots, a settling basin in
combination with grass infiltration areas.
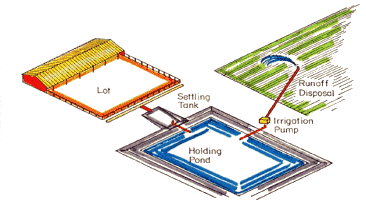 Equipment
to transfer and apply manure to cropland includes tanker wagons and trucks
that can spread manure on the surface or inject it directly beneath the
soil surface or irrigation systems with stationary or moving delivery systems.
Very dilute liquids can often be applied with irrigation systems. Equipment
to transfer and apply manure to cropland includes tanker wagons and trucks
that can spread manure on the surface or inject it directly beneath the
soil surface or irrigation systems with stationary or moving delivery systems.
Very dilute liquids can often be applied with irrigation systems.
 Back
to Beef Main Menu Back
to Beef Main Menu
|


 Equipment
to transfer and apply manure to cropland includes tanker wagons and trucks
that can spread manure on the surface or inject it directly beneath the
soil surface or irrigation systems with stationary or moving delivery systems.
Very dilute liquids can often be applied with irrigation systems.
Equipment
to transfer and apply manure to cropland includes tanker wagons and trucks
that can spread manure on the surface or inject it directly beneath the
soil surface or irrigation systems with stationary or moving delivery systems.
Very dilute liquids can often be applied with irrigation systems.