|
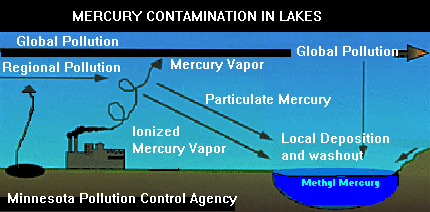
Mercury can enter water by many different routes and processes:
- wet and dry atmospheric depositions
- particle flux to sediments
- dissolved species exchange at sediment/water interfaces
- gas exchange at air/water/surface interfaces
- moving dissolved species exchange and particle flux via stream
and rivers
- dissolved species exchange via runoff
from groundwater to lakes
- direct discharge
of dissolved species via groundwater to lakes
- gas exchange at soil-air ion
interfaces
|