Introduction to the ISO 14000 Family
of Environmental Management
Standards
 |
By Poul Buch Jensen
Mr. Jensen represents INEM in ISO TC 207/SC 2, which
developed ISO 14015: Environmental assessment of sites and
organizations (EASO), and in a Working Group of ISO/TC 207/SC2, which
is preparing ISO 19011: Guidelines on Quality and Environmental
Management Systems Auditing. |
Illustrations adapted from Svend Fritjy
Andersson
Preface, Scope
The ISO 14000 family of environmental management standards, according to the
present plan, comprises 23 individual standards, guidelines and technical
reports related to environmental management in a company's environmental
management system (EMS). Consequently, they cover all areas of environmental
significance. Companies will thus be able to use the standards in connection
with activities offering:
- Savings when improving environmental conditions;
- Increased sales by presenting an environmental responsible behavior
towards the customers;
- Marketing advantages by offering the customers the cooperation with a
subcontractor/contractor that demonstrate competence in environmental
management - possibly substantiated by an environmental management
certificate.
Go
to top
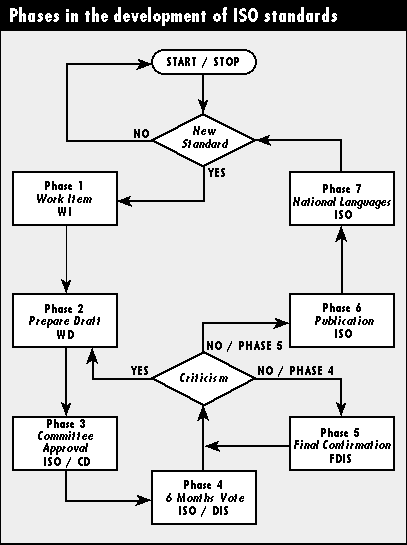
How Environmental Management Standards are Prepared
The International Organization for Standardization's Technical Committee 207
(ISO/TC 207) prepares environmental management standards in working group
activities in subcommittees. Subcommittee members are representatives from the
national committees. The standards are developed in phases as diagrammed and
described below.
Phase 1: Selection of Work Item. National Committees can propose new
Work Items (WI). All Work Items in ISO/TC 207 are registered and published in
yearly ISO reports.
Phase 2: Preparation of Working Draft. Working Drafts (WD) are
prepared by the working groups of the subcommittees. National committees,
participating with experts, receive all prepared Committee Drafts from the
relevant ISO Technical Committees.
Phase 3: Committee Approval of Working Draft. A vote is taken in
ISO/TC 207 on the Working Draft. Representatives of national organizations are
Participating Members and thus entitled to vote. If approved, it becomes a
Committee Draft. Representatives of national organizations are Participating
Members and thus entitled to vote. The vote is conducted after national
hearings, i.e. publication of the Committee Draft for comments to the proposed
standard. Approval of the Draft Standard requires at least a 2/3 majority of
Participating Members and a 3/4 majority of all ISO member countries
(Participating Members + others). The national committees prepare the
national responses to ISO/TC 207. More votes may be required if the hearings
result in significant amendments.
Phase 4: Ratification by all ISO members. The approved Committee Draft
is then sent to all ISO members for ratification as a Draft International
Standard (DIS). The voting period is six months.
Phase 5: Final confirmation. "En route" is a further affirming
vote. Following approval by the national ISO member countries, the document is
called a Final Draft International Standard (FDIS).
Phase 6: Publication of the ISO Standard. The approved standard is
published in Geneva in the official ISO languages: English, French and
Russian.
Phase 7: Publication in languages other than English, French and
Russian. The national committees will participate in the translation of the
standard into their national languages. The standard will subsequently be
published as national standards.
Note - For the current 18 member countries of either the European
Union or EFTA, the European Commission has decided to substitute technical
documentation in directives with references to standards. Comité Européen de
Normalisation (CEN) regulations stipulate that European standards (EN)
predominate in the member countries.
Go to
top
Overview of the ISO 14000 Family
The following chart presents the ISO 14000 family of environmental management
standards and names the ISO/TC 207 subcommittees responsible for preparing them.
Please visit the official ISO/TC 207 website
for information on the current status of the individual ISO 14000
standards.
|
ISO
No. |
Title of
International Standard / Guideline /
Technical Report |
Publication
Date |
Subcommittee |
|
ISO
14001 |
Environmental management
systems - Specification with guidance for use |
September
1996 |
SC 1/WG
1 |
|
ISO
14004 |
Environmental management
systems - General guidelines on principles, systems and supporting
techniques |
September
1996 |
SC 1/WG
2 |
|
ISO/AWI
14004 |
Revision of ISO 14004:1996 |
To be
determined |
SC 1/WG
2 |
|
ISO
14010 |
Guidelines for
environmental auditing - General principles |
October
1996 |
SC 2/WG
1 |
|
ISO
14011 |
Guidelines for
environmental auditing - Audit procedures - Auditing of environmental
management systems |
October
1996 |
SC 2/WG
2 |
|
ISO
14012 |
Guidelines for
environmental auditing - Qualification criteria for environmental
auditors |
October
1996
Corrected and reprinted
October 1998 |
SC 2/WG
3 |
|
ISO
14015 |
Environmental management
- Environmental assessment of sites and organizations (EASO) |
November
2001 |
SC
2 |
|
ISO/DIS
19011 |
Guidelines for quality
and/or environmental management systems auditing |
July
2001
|
ISO/TC
176/ SC 3
and
ISO/TC 207/SC 2 |
ISO 14020
2nd
Edition |
Environmental labels and
declarations - General principles |
September
2000 |
SC 3/WG
3 |
|
ISO
14020: 1998/DAM1 |
Draft amendment 1 to ISO 14020:1998 |
December
1998 |
SC 3 |
|
ISO
14021 |
Environmental labels and
declarations - Self-declared environmental claims (Type II environmental
labelling) |
September
1999 |
SC 3/WG
2 |
|
ISO
14024 |
Environmental labels and
declarations - Type I environmental labelling - Principles and
procedures |
April
1999 |
SC 3/WG
1 |
|
ISO/TR
14025 |
Environmental labels and
declarations - Type III environmental declarations |
March
2000 |
SC 3/WG
1 |
|
ISO
14031 |
Environmental management
- Environmental performance evaluation - Guidelines |
November
1999 |
SC 4/WG 1
&
SC 4/WG 2 |
|
ISO/TR
14032 |
Environmental management
- Examples of environmental performance evaluation |
1999 |
SC 4/WG
3 |
|
ISO
14040 |
Environmental management
- Life cycle assessment - Principles and framework |
June
1997 |
SC 5/WG
1 |
|
ISO
14041 |
Environmental management
- Life cycle assessment - Goal and scope definition and inventory
analysis |
October
1998 |
SC 5/WG
1 |
|
ISO
14042 |
Environmental management
- Life cycle assessment - Life cycle impact assessment |
March
2000 |
SC 5/WG
4 |
|
ISO
14043 |
Environmental management
- Life cycle assessment - Life cycle interpretation |
March
2000 |
SC 5/WG
5 |
ISO/WD
TR
14047 |
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Examples
of application of ISO 14042 |
1999 |
SC 5 |
ISO/CD
TR
14048 |
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Life
cycle assessment data documentation format |
1999 |
SC 5 |
|
ISO/TR
14049 |
Environmental management
- Life cycle assessment - Examples of application of ISO 14041 to goal and
scope definition and inventory analysis |
March
2000 |
SC 5/WG
3 |
|
ISO
14050 |
Environmental management
- Vocabulary |
May
1998 |
SC 6/WG
1 |
|
ISO 14050:
1998/DAM1 |
Draft amendment 1 to ISO 14050:1998 |
December
1999 |
SC 6 |
|
ISO/TR
14061 |
Information to assist
forestry organizations in the use of Environmental Management System
standards ISO 14001 and ISO 14004 |
December
1998 |
SC 5/WG
5 |
|
ISO/AWI
14062 |
Guidelines for integrating environmental aspects into
product development |
To be
determined |
SC 5 |
|
ISO Guide
64 |
Guide for the inclusion
of environmental aspects in product standards |
March
1997 |
SC 7/WG
1 |
Source: QA-061\6th Edition\2000-02-20 © BJQM ApS
The ISO 14000 family may be categorized into seven major groups as shown
in the chart below. A description of each standard, by group, follows.
| ISO 14000 Family of
Standards |
| GROUP |
STANDARDS |
| Environmental Management Systems |
ISO 14001
ISO 14004
ISO/TR 14061 |
| Environmental Auditing |
ISO 14010
ISO 14011
ISO 14012
ISO 14015
ISO 19011 |
| Environmental labelling |
ISO 14020
ISO 14021
ISO 14024
ISO/TR 14025 |
| Environmental Performance Evaluation |
ISO 14031
ISO/TR 14032 |
| Life Cycle Assessment |
ISO 14040
ISO 14041
ISO 14042
ISO 14043
ISO/TR
14047
ISO/TR 14048
ISO/TR 14049 |
| Environmental Management Vocabulary |
ISO 14050 |
| Environmental Aspects in Product Standards |
ISO 14062
ISO Guide 64 |
Environmental Management Systems
ISO 14001
Environmental management systems - Specification with guidance for
use
Scope: This International Standard specifies requirements for an
environmental management system, to enable an organization to formulate a policy
and objectives taking into account legislative requirements and information
about significant environmental impacts. It applies to those environmental
aspects which the organization can control and over which it can be expected to
have an influence. It does not itself state specific environmental performance
criteria.
This International Standard is applicable to any organization that wishes
to
- implement, maintain and improve an environmental management
system;
- assure itself of its conformance with its stated environmental
policy;
- demonstrate such conformance to others;
- seek certification/registration of its environmental management system by
an external organization;
- make a self-determination and self-declaration of conformance with this
International Standard.
All the requirements in this International Standard are intended to be
incorporated into any environmental management system. The extent of the
application will depend on such factors as the environmental policy of the
organization, the nature of its activities and the conditions in which it
operates. This International Standard also provides, in Annex A, informative
guidance on the use of the specification.
The scope of any ISO 14001 application must be clearly identified.
Note - For ease of use, the subclause of the specification and Annex A
have related numbers; thus, for example, 4.3.3 and A.4.3.3 both deal with
environmental objectives and targets, and 4.5.4 and A.4.5.4 both deal with
environmental system audit.
ISO 14004
Environmental management systems - General guidelines on principles,
systems and supporting techniques
Scope: This International Standard provides guidance on the
development and implementation of environmental management systems and
principles, and their coordination with other management systems.
The guidelines in this International Standard are applicable to any
organization, regardless of size, type or level of maturity, that is interested
in developing, implementing and/or improving an environmental mangement
system.
The guidelines are intended for use as a voluntary, internal management tool
and are not intended to be used as EMS certification/registration
criteria.
ISO/AWI
14004
Environmental management systems - General
guidelines on principles, systems and supporting techniques
Revision of ISO 14004.
Scope: See ISO 14004.
ISO/TR
14061
Information to assist forestry organizations in the use of
Environmental Management System standards ISO 14001 and ISO 14004
Scope: Informative reference material to assist forestry organizations
in the use of ISO 14001 and ISO 14004 environmental management system
standards.
Informative reference material to assist forestry organizations in the use of
ISO 14001 and ISO 14004 environmental management system standards.
Go to
top
Environmental Auditing
ISO 14010
Guidelines
for environmental auditing - General principles
Scope: This International Standard provides the general principles of
environmental auditing that are applicable to all types of environmental audits.
Any activity defined as an environmental audit in accordance with this
International Standard should satisfy the recommendations given in it.
ISO
14011
Guidelines for environmental auditing - Audit procedures -
Auditing of environmental management systems
Scope: This International Standard establishes audit procedures that
provide for the planning and conduct of an audit of an EMS to determine
conformance with EMS audit criteria.
ISO
14012
Guidelines for environmental auditing - Qualification criteria
for environmental auditors
Scope: This International Standard provides guidance on qualification
criteria for environmental auditors and lead auditors and is applicable to both
internal and external auditors. Criteria for the selection and composition of
audit teams are not included, reference is made to ISO 14011 for information on
these subjects.
Note - This International Standard has been developed in parallel with
the development of ISO standards on general principles of environmental auditing
(ISO 14010) and on guidelines for auditing of environmental management systems
(ISO 14011) specifically. It may require revision, if and when ISO develops
detailed guidance on other types of environmental audits.
ISO
14015
Environmental management -
Environmental assessment of sites and organizations (EASO)
Scope: This International Standard provides guidance on how to conduct
an EASO through a systematic process of identifying environmental aspects and
environmental issues and determining, if appropriate, their business
consequences.
This International Standard covers the roles and responsibilities of the
parties to the assessment (the client, the assessor and the representative of
the assessee), and the stages of the assessment process (planning, information
gathering and validation, evaluation and reporting). The process for conducting
an EASO is shown in Figure 1.
This International Standard does not provide guidance on how to conduct other
types of environmental assessment, such as:
a) initial environmental reviews;
b) environmental audits (including environmental management system and
regulatory compliance audits);
c) environmental impact assessments; or
d) environmental performance evalutions.
Intrusive investigations and site remediation, as well as the decision to
proceed with them, are outside the scope of this International Standard.
This International Standard is not intended for use as a specification
standard for certification or registration purposes or for the establishment of
environmental management system requirements.
Use of this International Standard does not imply that other standards and
legislation are imposed on the client or the assessee.
Figure 1 - Process for conducting an Environmental Assessment of Sites and
Organizations
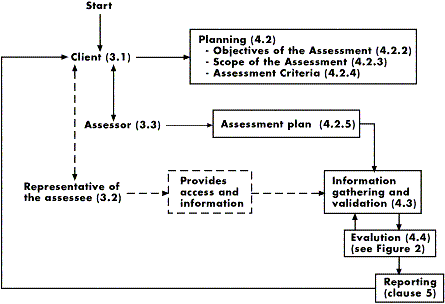
NOTE - The numbers between brackets refer to (sub)clauses in this
International Standard. The dashed lines indicate that the assessee is not
necessarily involved in an EASO as described in this International Standard (see
not to 3.2)
ISO/DIS
19011
Guidelines for quality and/or environmental management systems
auditing
Scope: This International Standard provides guidance on the principles
of auditing, the management of audit programs, the conduct of quality management
system audits and environmental management system audits as well as the
competence of quality and environmental management system auditors.
It is applicable to all organizations having a need to conduct and manage
internal or external quality and/or environmental management system audits.
The application of this International Standard to other types of audits is
possible in principle but special consideration should be paid to defining the
competence needed by the audit team members in such cases.
Go to
top
Environmental labelling
ISO
14020
Environmental labels and declarations - General principles
Scope: This International Standard establishes guiding principles for
the development and use of environmental labels and declarations. It is intended
that other applicable standards in the ISO 14020 series be used in conjunction
with this International Standard.
This International Standard is not intended for use as a specification for
certification and registration purposes.
Note - Other International Standards in the series are intended to be
consistent with the principles set forth in this International Standard. Other
standards currently in the ISO 14020 series are ISO 14021, ISO 14024 and ISO/TR
14025.
ISO
14021
Environmental labels and declarations - Self-declared
environmental claims (Type II environmental labelling)
Scope: This International Standard specifies requirements for
self-declared environmental claims, including symbols, regarding products. It
further describes selected terms commonly used in environmental claims and gives
qualifications for their use. This standard also describes a general evaluation
and verification methodology for self-declared environmental claims and specific
evaluation and verification methods for the selected claims in this
standard.
The standard does not preclude, override, or in any way change, legally
required environmental information, claims or labelling, or any other applicable
legal requirements.
ISO
14024
Environmental labels and declarations - Type I Environmental
labelling - Principles and procedures
Scope: This International Standard contains guiding principles and
practices, criteria procedures and guidance for certification procedures for the
development of multiple criteria-based, third party environmental labelling
programs (Type I). It is intended to provide practitioners and stakeholders with
a reference document ensuring the credibility and nondiscriminatory nature of
the program.
This International Standard aims at reducing environmental burden by
promoting market-driven demand for and supply of product meeting a
multiple-criteria based environmental labelling program, verified by a third
party.
ISO/TR
14025
Environmental labels and declarations - Type III environmental
declarations
Scope: This Technical Report identifies and describes elements and
issues concerning Type III environmental declarations and corresponding
programmes, including technical considerations, declaration format and
communication, and adminstrative considerations for developing and/or issuing a
Type III environmental declaration.
Go to
top
Environmental Performance Evaluation
ISO
14031
Environmental management - Environmental performance evaluation
- Guidelines
Scope: This International Standard gives guidance on the design and
use of environmental performance evaluation within an organization. It is
applicable to all organizations, regardless of type, size, location and
complexity.
This International Standard does not establish environmental performance
levels. It is not intended for use as a specification standard for certification
or registration purposes or for the establishment of any other environmental
management system conformance requirements.
ISO/TR
14032
Environmental management - Examples of environmental performance
evaluation
Scope: This document provides examples from real organizations to
illustrate the use of the guidance in ISO 14031.
Go to
top
Life Cycle Assessment
ISO
14040
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Principles
and framework
Scope: This International Standard specifies the general framework,
principles and requirements for conducting and reporting life cycle assessment
studies. This International Standard does not describe the life cycle assessment
technique in detail.
ISO
14041
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Goal and
scope definition and inventory analysis
Scope: This International Standard in addition to ISO 14040 specifies
the requirements and the procedures necessary for the compilation and
preparation of the definition of goal and scope for a Life Cycle Assessment
(LCA), and for performing, interpreting and reporting a Life Cycle Inventory
analysis (LCI).
ISO
14042
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Life cycle
impact assessment
Scope: This International Standard describes and gives guidance on a
general framework for the life cycle impact assessment (LCIA) phase of life
cycle assessment (LCA), and the key features and inherent limitations of LCIA.
It specifies requirements for conducting the LCIA phase and the relationship of
LCIA to the LCA phases.
ISO
14043
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Life cycle
interpretation
Scope: This International Standard provides requirements and
recommendations for conducting the life cycle interpretation phase in LCA or LCI
studies.
This International Standard does not describe specific methodologies for the
life cycle interpretation phase of LCA and LCI studies.
ISO/WD TR
14047
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Examples of
application of ISO 14042
Scope: Not yet available.
ISO/CD TR
14048
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Life cycle
assessment data documentation format
Scope: This document provides information regarding the formatting of
data to support life cycle assessment.
ISO/TR
14049
Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Examples of
application of ISO 14041 to goal and scope definition and inventory
analysis
Scope: This Technical Report provides examples about practices in
carrying out a Life Cycle Inventory analysis (LCI) as a means of satisfying
certain provisions of ISO 14041. These examples are only a sample of the
possible cases satisfying the provisions of the standard. They should be read as
offering a way or ways rather than the unique way of applying the standard. Also
they reflect only certain portions of an LCI study.
It should be noted that the examples presented in this Technical Report are
not exclusive and that many other examples exist to illustrate the
methodological issues described. The examples are only portions of a complete
LCI study.
Go to
top
Environmental Management Vocabulary
ISO
14050
Environmental management - Vocabulary
Scope: This International Standard contains definitions of fundamental
terms related to environmental management, published in the ISO 14000 series of
standards.
ISO 14050:
1998/DAM 1
Environmental management - Vocabulary
Amendment 1
Scope: See ISO 14050.
Go to
top
Environmental Aspects in Product Standards
ISO/AWI
14062
Guidelines for integrating environmental aspects into product
development
Scope: Not yet available.
ISO Guide
64
Guide for the inclusion of environmental aspects in product
standards
Scope: This Guide covers the consideration of environmental impacts in
product standards. It is intended for standard writers; its purpose is:
- to raise awareness that provisions in product standards can affect
the environment in both negative and positive ways;
- to outline the relationship between product standards and the
environment;
- to help avoid provisions in product standards that may lead to
adverse environmental impacts;
- to emphasize that addressing environmental aspects during the
development of product standards is a complex process and requires balancing
competing priorities; and
- to recommend the use of life-cycle thinking and recognized
scientific techniques when addressing environmental aspects of a product being
standardized.
In order to achieve the purposes listed under Scope, this Guide:
- sets forth some general considerations that should be taken into
account when developing product standards that achieve a proper balance
between product function and environmental impacts;
- outlines ways in which provisions in product standards may affect
the environment during the stages of a product's life cycle;
- addresses techniques for identifying and assessing the
environmental impacts of provisions in product standards;
- highlights some ways to reduce adverse environmental impacts
resulting from provisions in product standards.
To reflect the diversity of environmental effects that products can have,
this Guide may need to be supplemented with sectional guides.
Go to
top
Structure of ISO 14001
ISO 14001 has a clear and logical structure which covers the following:
- Scope
- Normative references
- Definitions
- Environmental management system requirements
4.1 General requirements
4.2 Environmental policy
4.3 Planning
4.4
Implementation and operation
4.5 Checking and corrective action
4.6
Management review
Annex A: Guidance on the use of the specification
Annex B: Links between ISO 14001 and ISO 9001
Annex C: Bibliography
Go to
top
Abbreviations used in the Standards
AWI = Approved Working Item
CD = Committee Draft. A CD is published in order to conduct a
CD-voting.
CD-voting = The national organizations (e.g., British Standards
Institute), which are P-members (participation members) and thus entitled
to vote, will cast their votes concerning the CD. A 2/3 majority is
required for the approval of a Committee Draft (CD). When the Committee Draft is
approved, it becomes a DIS (see: "DIS"), which is then sent out for
voting in all member countries.
CEN = Comité Européen de Normalisation
CENELEC = Comité Européen de Normalisation Electrotechnique
DIS = Draft International Standard. Draft for an International
Standard, approved in a relevant technical committee, and sent out for voting in
all ISO member countries. When approved by voting, the DIS becomes an
IS.
EN = European standard. It is expected that all the standards in the
ISO 14000 family will be approved as ENs.
FDIS = Final Draft International Standard
IEC = International Electrotechnical Commission
IS = International Standard
ISO = International Organization for Standardization
JWG = Joint Working Group. Here, ISO/TC 207 (Environmental Management)
and ISO/TC 176 (Quality Management), which is preparing ISO 19011: Guidelines on
Quality and Environmental Auditing.
LCA = Life Cycle Assessment
LCI = Life Cycle Inventory analysis
LCIA = Life Cycle Impact Assessment
NP = New Work Item Proposal
P-members = (P = Participating) National organizations, participating
in the preparation and voting on the Committee Drafts (CD) - prior to the
voting in all the ISO member countries.
prEN = Draft (project) for European Standard published for voting
amongst the CEN members.
SC = Sub Committee to a Technical Committee
TC = Technical Committee in ISO (e.g., ISO/TC 207 = Environmental
Management, ISO/TC 176 = Quality Management)
TR = Technical Report
WD = Working Draft
WG = Working Group
WI = Work Item
Go to
top
about the Author
Poul Buch Jensen is director of the consulting firm Buch Jensen
Quality Management ApS in Denmark, with more than 25 years of experience in the
quality management field, and author of numerous articles and books on
implementation of ISO 9000 and ISO 14001. He is a Liaison A member of ISO TC 207
(Environmental Management Standards) and a member of the American Society of
Quality Control. Mr. Jensen is a certified quality assessor and the former
manager for systems certification in the Danish Standards Association.
Contact:
Buch Jensen Quality Management ApS
Alfarvejen 30 - Osted
DK-4000
Roskilde
Denmark
Tel.: +45-4649-8044
Fax: +45-4649-8233
Email: poul@buchjensen.dk
Home Page: http://www.buchjensen.dk/
Go to
top
Contact INEM ( info@inem.org )
Page
last updated 20 November 2001
Copyright © 1998 - 2001 International Network
for Environmental Management