Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Miscellaneous
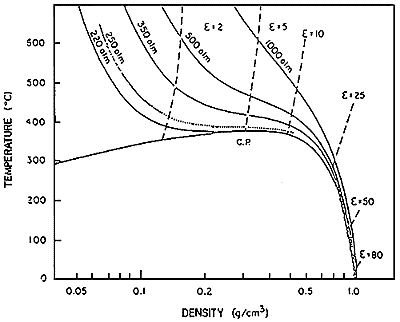
Water, most important solvent in nature, has fascinating properties as a reaction solvent in its super critical condition. The super critical water is the fluid that is over the critical point of vapor-liquid coexistence state. The critical temperature and critical pressure of water are 647K and 22MPa, respectively. The density of super critical water can continuously be controlled between gas like and liquid like values by varying its pressure and temperature. The value of dielectric constant that is one of the parameter estimating the solvent polarity, increase with increasing density. The relation between dielectric constant and density is shown in Figure 11). At super critical condition, the values of the constant between 5 to 25 can be obtained. This corresponds to the dielectric properties of polar organic liquids under normal condition. This property partially explain its ability to dissolve nonpolar organic compounds.
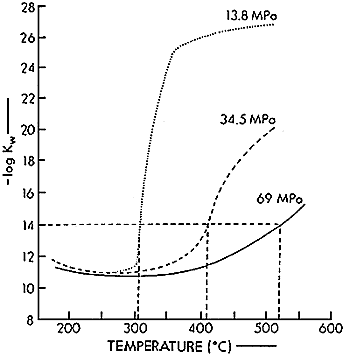
At standard conditions, water dissociates slightly into hydrated hydrogen and hydroxyl ions: the "ion product" (Kw) of their concentrations is about 10-14(mol /1)2. The ion product of water is strongly dependent on density and weakly dependent on temperature. This is shown in Figure 22). At super critical condition, for example at 573K and 34.5MPa, the value of ion product is 10-11. This value means hydrogen ion concentration of super critical water is almost 3*10-7 and this value means that the super critical water at this condition acts the role as acid solutions catalyst.
Fig.1 Dielectric constant of water
Fig.2 Ion product of water
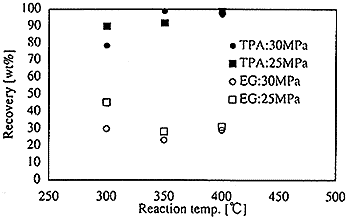
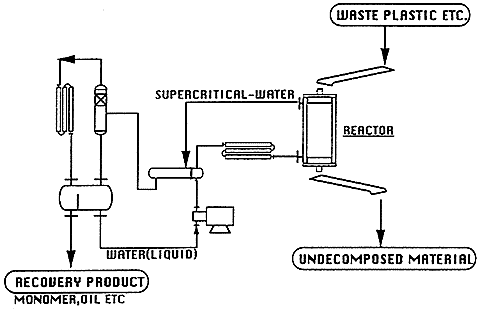
By the fascinating properties of super critical water, the substance with ether, ester and isocyanate bond which are the condensation polymerization plastic can easily be decomposed to their monomer when super critical water is used as reaction solvent. It is experienced that the PET(Polyethylene terephthalate) is decomposed to their monomer in the super critical water by the batch-continuous apparatus. Fig.3 shows the relation between the recovery yield of monomer and reaction temperature at 25MPa and 30MPa. The recovery yield of TPA ( Terephthalic acid ) reaches almost 100% over 350K of the temperature. However, yield of EG ( Ethylene glycol ) is about 30% at the same temperature. It seems that this due to effect of acid catalyst of recovered TPA in super critical water.
Fig.3 Relation between recovery yield of TPA from PET and reaction temperature at 25, 30MPa
When the super critical water is used as reaction solvent, the temperature of water used as reaction medium is over the pyrolysis condition of plastics. The addition polymerization plastic is converted to the oil in the super critical water. The representative addition polymerization plastics are PP(Polypropylene), PE(Polyethylene), etc.
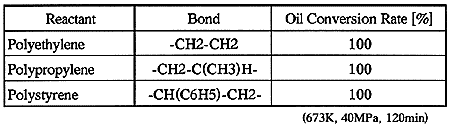
Table 1 Decomposition Product of Polymer in Super critical Water
When the waste material which is composed of the condensation polymerization plastic and the addition polymerization plastic, is treated in the super critical water, the former one is selectively decomposed to their monomer in short time, that is the chemicals, and at this time latter one is not decomposed. The addition polymerization polymer, however, is continuously converted to oil following to the monomerization of the condensation polymerization plastic. The technology on this decomposition of plastics in the super critical water is expected as the novel waste material treatment process.
LITERATURE CITED
1. Property of super critical water
2. Hydrolysis of plastic in super critical water
3. Pyrolysis of plastic in super critical water
The experimental result is shown in Table 1.
4. Application off super critical water in waste plastic treatment field
1) R. W. Shaw, et. al., C & EN, 23 (12), 26 (1991)
2) E. U. Franck, Pure Appl. Chem., 24 (1), 13 (1970)