Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Ash Handling
- Utilization of Slag
- Longer Service Life of Electrodes
- Easy to Operate System
- Industrial Solid Waste Treatment Facilities
- Areawide Solid Waste Treatment Facilities (Atomic Waste Treatment Facilities)
- Plasma Fusion Center at Kitayazu Refuse Incineration Plant in Chiba City
Capacity 1,000kg/h , Torch Output 1,000kW
[General]
Municipal solid waste have been annually increasing in both terms of generated amount and versatility for its kinds, but on the other hand, it is true that they have been reduced in actual volume through the implementation of incineration disposal.
However, there are still problems to be dissolved such as lacking of sufficient disposal sites for incineration ash, and environmental pollution that is arising in the area of the disposal sites. Thus, the issues of waste reduction, harmlessness and recycling of incineration ash have been urgent subjects to be taken care of.
We developed the Plasma Type Incinerated Ash Fusion System jointly with the Tokyo Electric Power Co., Ltd. and Kawasaki Steel Corp. to dissolve all these unsolved problems at the same time. Currently, a demonstration facility is working in Chiba City (Kitayazu), Japan.
[Operating Principle]
First, sparks are to be generated within the plasma torch to obtain plasma working gas. A stable plasma flow is thus secured because the torch becomes conductive with the furnace bottom electrode due to this plasma working gas. The temperature of the plasma flow will be 20,000deg.C to 30,000deg.C at the center area, and it will be 3,000deg.C or over at the surface of the external cylinder. Such high temperature will easily enable fusion of the incineration ash (melting point: about 1,200 deg.C).
[Flow Sheet]
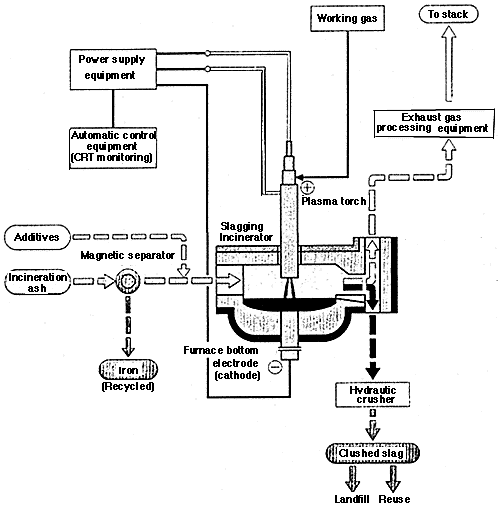
[Feature]
- Harmlessness and Volume Reduction
Incineration ash is melted by using high plasma temperature, and it is evenly slagged like glass to become a harmless material that is free from elution of heavy metal ingredients. Also, the volume will be reduced down to one-third in the case of slow cooling slag (cf. about one half in the case of hydropulping slag).
- Utilization of Clean Energy
This system efficiently utilize the surplus power generated by the municipal refuse incinerator, and the energy is much more clean and economical than other kind of fuels such as fossil fuel.
- Compact System in Size
[Capacity]
We completed demonstration in 1994 at a plant in Chiba City (Kitayazu), and currently there are various capacity types are available ranging from 20t/day to 100t/day, thus enabling to take care of wide range of customer's needs.
[Applicable Fields]
- Municipal Solid Waste Treatment Facilities, Domestic Waste Water Treatment
Facilities.
[Installation Examples]
- Experimental Facility at Steel Structure Research Center, Kawasaki Steel Corp.
Capacity 200kg/h , Torch Output 250kW
1-1 Higashikanasaki-cho 3-chome Chuo-ku Kobe 650-91 Japan
Tel : +81-78-360-8710 Fax : +81-78-360-8660