Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Ash Handling
1. Purpose
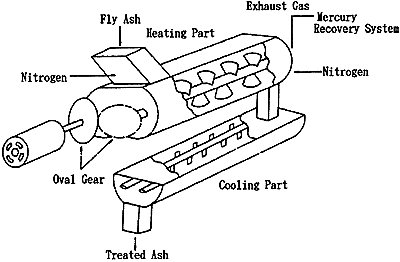
Dioxins contained in fly ash of a municipal solid waste incinerator are resolved by heating with high efficiency, while mercury is evaporated to make fly ash harmless. As shown in the figure below, fly ash is fed into and heated in the double shaft type paddle mixer where nitrogen is blown and dioxin resolution is occurred in poor-oxygen atmosphere, and is discharged after cooled down at the cooling part.
Mercury in the flue gas exhausted through the heating part is collected with mercury recovery system.
2. Performance
Dioxin resolution efficiency: > 99%
Dioxin density: < 0.1 ng TEQ/g of ash
Mercury removal efficiency: > 95%
Mercury density of the treated ash in the leaching test:
< 0.005 mg/l
Heated ash temperature: 400 - 450deg.C
Discharged ash temperature: < 60deg.C
3. Characteristics
High dioxin resolution efficiency can be achieved because double shaft equipment with effective stirring motion is used at both heating and cooling part. (Especially an oval gear with two shafts at the heating part enables the speed of revolution to be controlled in order to obtain an effective stirring motion.) The two equipments are connected closely so that the consumption of nitrogen gas is reduced .
Mercury evaporated into flue gas during dioxin resolution process is removed by the mercury recovery system.
4. Principle
In the presence of oxygen, dioxins are formed in fly ash of 300deg.C ~ 400deg.C, by chlorine originated from metal chloride reacting with aromatic compounds (Deacon reaction). However in poor-oxygen atmosphere dioxins are scarcely formed and dioxin resolution is accelerated.