Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Drying, Incineration and Melting
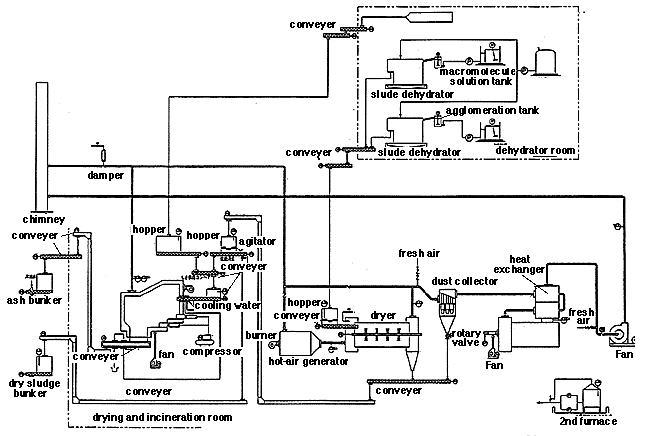
2) Drying ---------- Dehydrated sludge (water content: approx. 80%) -> Dehydrated
sludge (water content: approx. 30%)
3) Incineration ---- Dehydrated waste (water content: approx. 60%), dehydrated
sludge (water content: approx. 30%)
2) Hot exhaust gas from the incinerator furnace is used as the heat source,
saving the energy used to dry the dehydrated sludge.
3) Rotary drier with stirrer vanes ensures highly efficient drying operation.
4) Exhaust gas is deodorized by ample secondary combustion.
5) Waste-heat is collected by a heat exchanger to save fuel used in secondary
combustion.
6) Suitable hopper siting and conveyor operation allows various operation
patterns to be supported.
7) Installation of a hot-air furnace enables drying only.
8) Induction fans are located at the rear of the deodorizer furnace to prevent
leakage of combustion gases.
9) Furnace pressure control, temperature control, hopper level monitoring are
managed on the instrumentation panel to ensure safe running and operation.
Introduction
This drying and incinerating equipment processes dehydrated waste and sludge generated in sewage disposal plants. Once the dehydrated sludge is dried by incineration exhaust gas, it is incinerated or conveyed to outside the plant for recycling. Dehydrated waste is burned together with dried sludge in the incinerator.
Processes
1) Receiving ------- Dehydrated waste (water content: approx. 60%), dehydrated
sludge (water content: approx. 80%)
Features
1) Sturdy furnace pusher system ensures highly stable incineration.
Installation Example
- Dehydrated waste ------ 150 kg/hr (water content: 60%)
- Dehydrated sludge ----- 823 kg/hr (water content: 78%)
PLANT DIVISION
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Department 2
ShinOsaka Wako Bldg 7F
4-6-18 MIYAHARA YODOGAWA-KU
OSAKA 532 JAPAN
TEL:+81-6-350-3770 FAX:+81-6-350-3775