Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Drying, Incineration and Melting
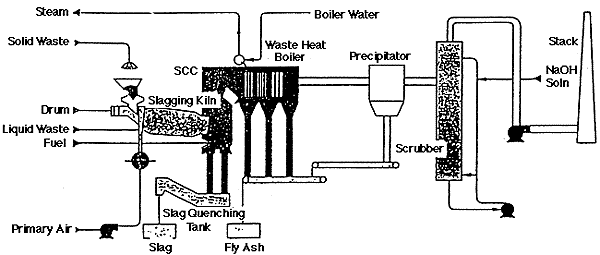
2. Wet scrubber type
(Abstract)
The rotary kiln is a horizontal cylinder, lined with refractory, which turns about its longitudinal axis. Waste is deposited in the kiln at one end and the waste burns out to an ash by the time it reaches the other end. Kiln rotation speed varies in the range of 0.05~0.5 revolutions per minute.
At temperatures above 1300 deg.C, ash will start to deform and as the temperature increases, the ash will melt. The actual temperatures of initial deformation and subsequent physical changes to the ash is a function of the chemical constituents present in the waste residual.
(Characteristics)
Perfect burning of hazardous waste such as chlorinated hydrocarbon.
Not leaching of heavy metal with slagging.
Most reduction volume with slagging.
Acceptable metal drum.
Less particulate.
Flexible on operation condition.
(Principle)
The hazardous waste that is incinerated consists mainly of the following types;
- Oil waste - Waste containing PCB
- Solvent and varnish waste - Pesticide waste
- Paint and varnish waste - Hazardous chemical remains
- Adhesive waste
The three most common requirements for efficient and environmentally safe incineration are;
- High combustion temperature
- Long flue gas detention time at a high temperature, and
- A well mixed excess of air (turbulence)
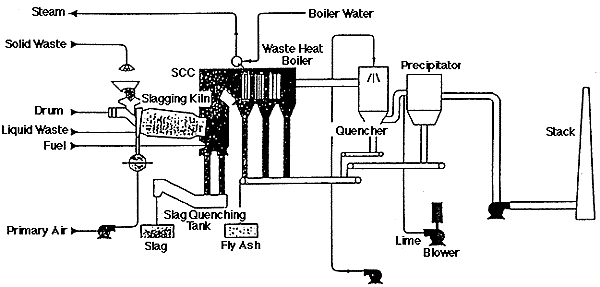
The incineration plant consists of;
- The input system - The exhaust gas boiler
- The control unit - Flue gas cleaning
- The rotary kiln - The chimney stack
- The post-combustion chamber
(Flow Sheet)
1. Dry scrubber type