Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Drying, Incineration and Melting
We have increased the reliability of refuse processing technology through the promotion of areas such as complete incineration system, the automation of peripheral systems and the implementation of energy conservation measures. In addition, we will continue to develop technology that will prevent secondary pollution through extensive treatment of flue gas, waste water and other discharges and provide a clean and safe environment of the employees of the plant and the people of the area it serves.
We can supply an incineration unit between 10 and 1,000 t/d and withstand between 800 and 3,500 kcal/kg of calorific value, allowing the processing of a wide range of wastes, both in quantity and in quality.
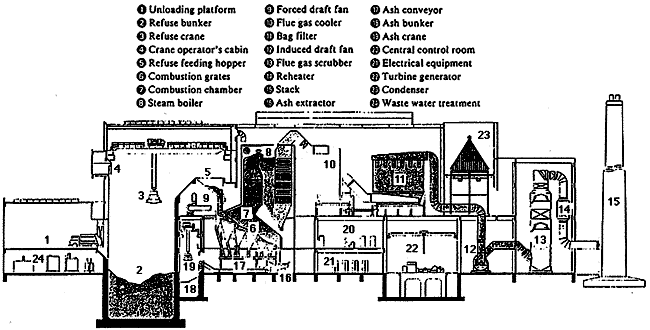
TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF REFUSE INCINERATION PLANT
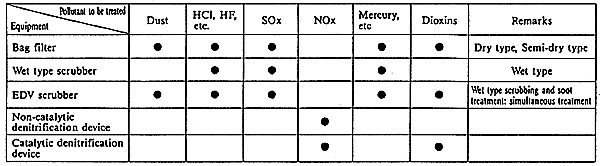
We can supply an extensive lille-up of flue gas treatment system. Emissions from the incilleration process can be controlled with proven techniques to any desired level in order to satisfy applicable environmental stalldard.
LINE-UP OF FLUE GAS TREATMENT SYSTEM
System 1 (Example)
System 2 (Example)
[Abstract]
Hitachi Zosen built Japan's first modern stoker type incineration plant for a large municipality in 1965, affiliated with Von Roll Ltd. During over the 30 years since then, we have continued nurture the technology needed for dealing with the issue of municipal waste disposal and have contlibuted to the development of more than 140 similar plants, both in Japan and abroad.
[Plant Process]
The incilleration plants are classified according to two types by flue gas cooling method. One is boiler type and the other is water injection type. The boiler type plant generates high pressure steam. Utilizing steam, the plant can supply electric power, heat and hot water for internal and for external use. In the water injection type plant, high temperature Alue gas is cooled down by water spraying into it. This type of plant can be operated by daily start and stop, and is maillly employed in a small municipality.
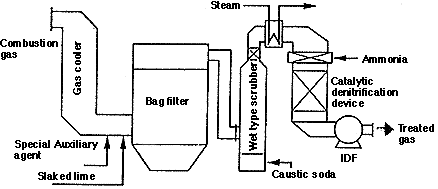
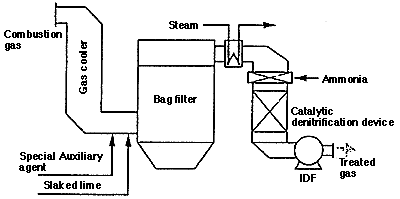
After the temperature of the exaust gas has been lowered in the temperature control tower, lime and a special auxiliary agent are blown in. The bag filter then removes dust as well as HCl, Sox, mercury, dioxin, etc.
In addition to the process described above, this system uses a wet type scrubber to remove HCl, SOx and mercury from the exhaust gas afer it has passed through the bag filter.