Waste Treatment Technology in JAPAN
Drying, Incineration and Melting
2) Complete Incineration of Waste
3) High Combustion Efficiency and Small Excess Air Ratio
4) Easy Start and Stop
5) Easy Mixed Combustion of Waste and Sludge
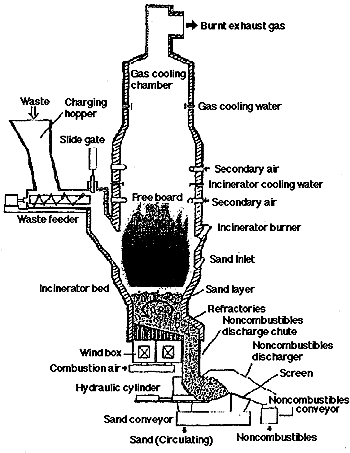
Structure of Mitsubishi Fluidized Bed incinerator
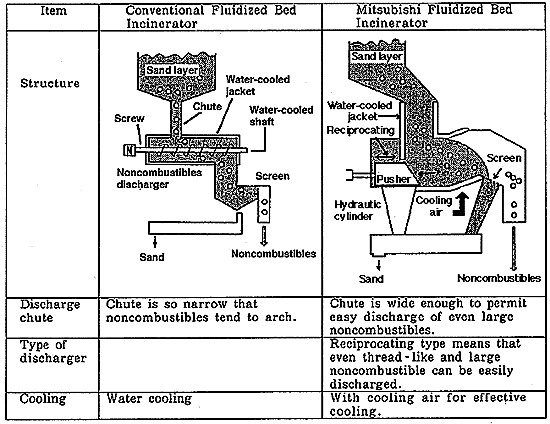
(2) A reciprocating discharger for noncombustibles is used to prevent
entanglement of thread-like noncombustibles.
(3) Cooling air is supplied to the discharger to increase the cooling
effect.
Table 1 Comparison of Noncombustible Discharger
1. Purpose
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. has supplied 46 fluidized bed incinerators for disposing of sludge and industrial wastes since 1971.
With many years of experience in fluidized bed incinerators for sludge, and so on mentioned above and in stoker furnaces, MHI aimed at establishing a system which would defy comparison with others in terms of ease of maintenance and management, energy conservation, and pollution-free performance. MHI successfully developed it in 1989. The first fluidized bed waste incinerator based on the above system was built in February 1994 for the Kansai International Airport.
2. Characteristics
1) Drying, ignition, and combustion all in an instant
The red hot sand moves violently up and down in the incinerator and the waste thrown into it is dried, ignited, and burnt out instantaneously by contact with the sand. Thus, the incinerator has a high incineration ratio per unit area of the bed.
Waste is burnt on contact with the fluidized sand and the residue in ash and noncombustibles move along with the fluid motion of the sand to be taken out of the ash chute at the bottom. This ensures complete combustion, and reduces unburnt rate of ash to less than 1%.
Heat is transferred to the waste by contact with a large amount of fluidized sand so that the heat transfer speed is high. It cannot be evaluated in the same way as the fire grate combustion rate for the stocker furnace, but considering that the bed combustion rate may be assumed to be about 450 kg/m2h, the incinerator can be compactly designed. The excess air ratio can be lowered to reduce the amount of exhaust gas.
The sand layer in the incinerator stores heat so that incinerator temperature falls at a slow rate after shutdown. If it is restarted after a short period of shutdown (about one day, for example), waste can be charged into the incinerator from the beginning and be completely burnt .
The incinerator can be easily shut down by simply stopping charging waste because it is instantly burnt as soon as it is charged into it. This dispenses with such operation as banking boiler and eliminates soot and foul odors after incinerator shutdown.
The Fluidized bed incinerator has been mostly used for burning sludge that contains a large amount of water. In this case, combustion is stable through contact with the fluid sand that stores intense heat. When burning waste and sludge together, therefore, sludge may be directly thrown into the incinerator and the mixture will be burnt completely with ease.
3. Noncombustibles Discharger
While MHI succeeded in technically solving the problems of the conventional
fluidized bed incinerator, particularly about the conveyance and discharge of noncombustibles over the incinerator bed, the conventional one has other problems in the processes downstream, that is, in the discharge of noncombustibles from the incinerator as large-sized noncombustibles form an arch on the way or thread-like noncombustible become stuck with the screw, causing incinerator shutdown.
The MHI fluidized bed incinerator employs a system that has a large - sized noncombustibles discharge function as efficient as that of the stocker furnace, developed from the idea of the ash dicharge unit that had been in use since 1975 for MHI Martin incinerators to deal with the fatal problem of incinerator shutdown.
(l) A wider noncombustibles discharge chute than the conventional
counterpart is employed.
These ingenious features add up to an effective discharge mechanism for noncombustibles .
A pretreatment crusher was essential to the conventional fluidized bed incinerator to ensure stable operation, but had the problems of troublesome maintenance and management and high running cost. The MHI fluidized bed incinerator, however, can treat noncombustibles free of trouble without a crusher. (See Table 1.)