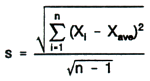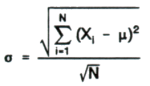Indoor Radon and Radon Decay
Product Measurement Device ProtocolsAccuracy: The degree of agreement of a measurement (X) with an accepted reference or true value (T); usually expressed as the difference between the two values (X – T), or the difference as a percentage of the reference or true value (100[X – T]/T), and sometimes expressed as a ratio (X/T).
Active radon/radon decay product measurement device: A radon or radon decay product measurement system which uses a sampling device, detector, and measurement system integrated as a complete unit or as separate, but portable, components. Active devices include continuous radon monitors, continuous working level monitors, and grab radon gas and grab working level measurement systems, but does not include devices such as electret ion chamber devices, activated carbon or other adsorbent systems, or alpha track devices.
Alpha particle: Two neutrons and two protons bound as a single particle that is emitted from the nucleus of certain radioactive isotopes in the process of decay.
Background instrument (analysis system, or laboratory) count rate: The nuclear counting rate obtained on a given instrument with a background counting sample. Typical instrument background measurements are:
- Unexposed carbon: for activated carbon measurement systems.
- Scintillaton vial containing scintillant and sample known to contain no radiactivity: for scintillation counters.
- Background measurements made with continuous radon monitors exposed only to radon-free air (aged air or nitrogen).
Background fields measurements (blanks): Measurements made by analyzing unexposed (closed) detectors that accompanied exposed detectors to the field. The purpose of field background measurements is to assess any exposure to the detector caused by radon exposure other than from the concentration in the environment to be measured. Results of background field measurements are subtracted from the actual field measurements before calculating the reported concentration. Background levels may be due to electronic noise of the analysis system, leakage of radon into the detector, detector response to gamma radiation, or other causes.
Background radiation: Radiation arising from radioactive material other than that under consideration. Background radiation due to cosmic rays and natural radioactivity is always present; background radiation may also be due to the presence of radioactive substances in building materials.
Becquerel (Bq): The International System of Units (SI) definition of Activity. 1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second.
Calibrate: To determine the response or reading of an instrument relative to a series of known values over the range of the instrument; results are used to develop correction or calibration factors.
Check source: A radioactive source, not necessarily calibrated, which is used to confirm the continuing satisfactory operation of an instrument.
Client: The individual or parties who hire(s) the radon tester.
Closed House Conditions: During any short-term test, closed-house-conditions should be maintained as much as possible while the test is in progress. In tests of less than 4 days duration, closed-house-conditions should be maintained for at least 12-hours before starting the test and for the duration of the test. While closed-house-conditions are not required before the start of tests that are between 4 and 90-days, closed-house-conditions should be maintained as much as possible.
Coefficient of variation (COV), relative standard deviation (RSD): A measure of precision, calculated as the standard deviation (s or s) of a set of values divided by the average (Xave or µ), and usually multiplied by 100 to be expressed as a percentage.
COV = RSD = / x 100 for a sample,
COV' = RSD' = / x 100 for a population
See Relative percent difference.
Curie (Ci): A standard measurement for radioactivity, specifically the rate of decay for a gram of radium – 37 billion decays per second. A unit of radioactivity equal to 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second.
Duplicate measurements: Two measurements made concurrently and in the same location, or side-by-side. Used to evaluate the precision of the measurement method.
Efficiency, Intrinsic detector: The relationship between the number of events recored (counts, voltage lost, tracks) and the number of radioactive particles incident up on the sensitive element of the detector per unit time. Efficiencies for radon detectors are commonly expressed in terms of the calibration factor, which is the number of events (counts) per time (our or minute) per radon concentration (pCi/L). Methods with high efficiencies will exhibit more counts (signal) per time in response to a given radon level than will a method with a low efficiency.
Equilibrium ration, radon: Equilibrium ratio = [WL(100)}/(pCi/L). At complete equilibrium (i.e., at an equilibrium ratio of 1.0), 1 WL of RDPs would be present when the radon concentration was 100 pCi/L. The ratio is never 1.0 ina house. Due to ventilation and plate-out, the RPDs never reach equilibrium in a residential environment. A commonly assumed equilibrium ratio is 0.5 (i.e., the decay products are halfway toward equilibrium), in which case 1 WL would correspond to 200 pCi/L. However, equilibrium ratios vary with time and location, and ratios of 0.3 to 0.7 are commonly observed.
Equilibrium equivalent concentration (EEC): The radon concentration in equilibrium with its short-lived progeny, that has the same potential alpha energy per volume as exists in the environment being measured (see working level).
Exposure time: The length of time a specific mail-in device must be in contact with radon or radon decay products to get an accurate radon measurement. Also called exposure period, exposure parameters, or duration of exposure.
Gamma radiation: Short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation of nuclear origin, with energies between 10 keV to 9 MeV.
Integrating device: A device that measures a single average concentration value over a period of time. Also called a time integrating device.
Lower limit of detection (LLD): The smallest amount of sample activity which will yield a net count for which there is confidence at a predetermined level that activity is present. For a five percent probability of concluding falsely that activity is present, the LLD is approximately equal to 4.65 times the standard deviation of the background counts (assuming large numbers of counts where Gaussian statistics can be used [ANSI 1989, Pasternack and Harley 1971, U.S. DOE 1990]).
Lowest Level suitable for occupancy: The lowest level currently lived in or a lower level not currently used, such as a basement, which a prospective buyer could use for living space without renovations. This includes a basement that could be used regularly, as for example a recreation room, bedroom, den, or playroom.
Lowest lived-in level: The lowest level or floor of a home that is used regularly, including areas such as family rooms, living rooms, dens, playrooms, and bedrooms.
Passive radon/radon decay product measurement device: A radon or radon decay product measurement system in which the sampling device, detector, and measurement system do not function as a complete, integrated unit. Passive devices include electret ion chamber devices, activated carbon or other adsorbent systems, or alpha track devices, but does not include continuous radon/radon decay product monitors, or grab radon/radon decay product measurement systems.
PicoCurie (pCi): One pCi is one trillionth of a Curie, 0.037 disintegrations per second, or 2.22 disintegrations per minute.
PicoCurie per liter (pCi/L): A unit of radioactivity corresponding to an average of one decay every 27 seconds in a volume of one liter, or 0.037 decays per second a liter of air or water. 1 pCi/L = 37 Becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m3).
Precision: A measure of mutual agreement among individual measurements of the same property, usually under prescribed and similar conditions. Most desirably expressed in terms of the standard deviation, but can be expressed in terms of the variance, pooled estimate of variance, range, relative percent difference, or other statistic.
Quality assurance: A complete program designed to produce results which are valid, scientifically defensible, and of known precision, bias, and accuracy. Includes planning, documentation, and quality control activities.
Quality control: The system of activities to ensure a quality product, including measurements made to ensure and monitor data quality. Includes calibrations, duplicate, blank, and spiked measurements, interlaboratory comparisons, and audits.
Radon (Rn): A colorless, odorless, naturally occurring, radioactive, inert, gaseous element formed by radioactive decay of radium (Ra) atoms. The atomic number is 86. Although other isotopes of radon occur in nature, radon in indoor air is primarily Rn-222.
Radon chamber: An airtight enclosure in which operators can induce and control different levels of radon gas and radon decay products. Volume is such that samples can be taken without affecting the levels of either radon or its decay products within the chamber.
Relative percent difference (RPD): A measure of precision, calculated by:
RPD = [(|X1 - X2 |)/Xave x 100
where:
X1 = concentration observed with the first detector or equipment;
X2 = concentration observed with the second detector, equipment, or absolute value;
|X1 - X2| = absolute value of the difference between X1 and X2; and
Xave = average concentration = ((X1 + X2) / 2)
The relative percent difference (RPD) and coefficient of variation (COV) provide a measure of precision, but they are not equal. Below are example duplicate radon results and the corresponding values of relative percent difference and coefficient of variation:
Rn1
(pCi/L)Rn2
(pCi/L)RPD
(%)COV
(%)8 9 12 8 13 15 14 10 17 20 16 11 26 30 14 10 7.5 10 29 20 Note that the RPD divided by the square root of 2 = COV
See Coefficient of variation (COV).
Relative standard deviation: See Coefficient of variation.
Sensitivity: The ability of a radon or WL measurement method to produce reliable measurements at low concentrations. This ability is dependent upon the variability of the background signal (counts not due to radon or WL exposure) which the method records, as well as its efficiency. Methods with stable background rates and high efficiencies will be able to produce reliable measurements at lower concentrations than methods with variable background rates and low efficiencies. Sensitivity can be expressed in terms of the lower limit of detection or minimum detectable activity.
Signal-to-noise ratio: For radon and WL detectors, this term expresses the proportion of the number of counts due to exposure to radon or WP (signal) to the number of counts due to background (noise). Measurement methods with high signal-to-noise ratios will produce more counts due to radon or WL exposure (signal) in proportion to the background counts (noise) than will methods with low signal-to-noise ratios. A method with a high signal-to-noise ratio is more likely to exhibit good sensitivity, i.e., be able to produce reliable measurements at low concentrations.
Spiked measurements, or known exposure measurements: Quality control measurements in which the detector or instrument is exposed to a known concentration and submitted for analysis. Used to evaluate accuracy.
Standard deviation (s): A measure of the scatter of several sample values around their average. For a sample, the standard deviation (s) is the positive square root of the sample variance:
For a finite population, the standard deviation (s) is:
where µ is the true arithmetic mean of the population and N is the number of values in the population. The property of the standard deviation that makes it most practically meaningful is that it is in the same units as the observed variable X. For example, the upper 95% probability limit on differences between two values is 2.77 times the sample standard deviation.
Standard operating procedure: A written document which details an operation, analysis, or action whose mechanisms are prescribed thoroughly and which is commonly accepted as the method for performing certain routine or repetitive tasks.
Statistical control chart, Shewhart control chart: A graphical chart with statistical control limits and plotted values (for some applications in chronological order) of some measured parameter for a series of samples. Use of the charts provides a visual display of the pattern of the data, enabling the early detection of time trends and shifts in level. For maximum usefulness in control, such charts should be plotted in a timely manner (i.e., as soon as the data are available).
Statistical control chart limits: The limits on control charts that have been derived by statistical analysis and are used as criteria for action, or for judging whether a set of data does or does not indicate lack of control. On a means control chart, the warning level may be two standard deviations above and below the mean, and the control limit may be three standard deviations above and below the mean.
Systeme Internationale (SI): The International System of Units as defined by the Conference of Weights and Measures in 1960.
Test Interference: The altering of test conditions prior to or during the measurement in order to change the radon or radon decay product concentrations or the altering of the performance of the measurement equipment.
Time Integrated measurement: A measurement conducted over a specific time period (e.g., from two days to a year or more) producing results representative of the average value for that period.
Uncertainty: The estimated bounds of the deviation from the mean value, expressed generally as a percentage of the mean value. Taken ordinarily as the sum of (1) the random errors (errors of precision) at the 95% confidence level, and (2) the estimated upper bound of the systematic error (errors of accuracy).
Working level (WL): Any combination of short-lived radon decay products in one liter of air that will result in the ultimate emission of 1.3 x 105 MeV of potential alpha energy. This number was chosen because it is approximately the alpha energy released from the decay products in equilibrium with 100 pCi of Ra-222. Exposures are measured in working level months (WLM).
Working level months (WLM): (working level x hours or exposure)/(170 hours/working month). In SI units, 1 WLM = 6 x 105 Bq-h/M3 (EEC).
Table of Contents || Section One || Section Two || Section Three || References
http://www.epa.gov/iaq/radon/pubs/devprot5.html
Created: July 29, 1999