
Australian Country Spinners, a wool spinning and dyeing company, has implemented a range of cleaner production initiatives that have improved the process efficiency and achieved significant cost savings. Over a three year period the company achieved a 44 per cent reduction in water usage and a 26 per cent reduction in chemical usage, per kilogram of processed yarn. These gains translated to savings in excess of $1.1 million.
- Mr John West,
- Technical Manager
- Australian Country Spinners Pty. Ltd.
- Textile Avenue
- Wangaratta, Victoria, 3677
- Ph: 61 57 21 2111
- Fax: 61 57 21 9523

Australian Country Spinners Pty. Ltd. (ACS), one of Australia's largest yarn manufacturers, is located at Wangaratta in rural Victoria. It produces in excess of 2,500 tonnes of finished yarn annually, with exports to New Zealand, Japan, USA and Korea. The company's manufacturing focus is principally directed towards fine quality wools, but other fibres are also processed.
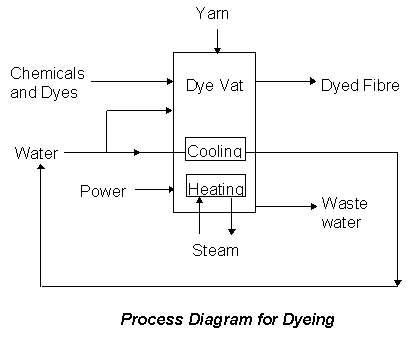
The wool dyeing industry is a large user of water, and traditionally up to one million litres of water was used daily by ACS. Each kilogram of finished yarn required 250 litres of water and three kilograms of chemicals.
Twenty different in-plant waste streams contributed to total effluent outfall from the ACS site, however, over half of the wastewater stream was generated from fibre rinsing operations. The effluent characteristics of greatest significance were total dissolved solids (TDS), biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), colour and toxicity. This effluent was discharged to the local waterway after treatment at a common treatment plant.
ACS commenced their cleaner production program in 1992 with a waste audit and preparation of a waste management plan (WMP). The audit measured all the waste streams, established mass balances across processes, identified potential areas for change and improvement and also opportunities for reductions in effluent volume. The findings from the audit provided the input for the development of the WMP. ACS established a team that was empowered to make changes to site operations and processes in order to implement the WMP objectives and cleaner production initiatives. Support was provided by top management for the involvement of the total workforce, including the provision of regular briefings to employees on cleaner production changes.
The company identified that approximately 90 per cent of its effluent was relatively clean. By segregating the waste streams ACS was able to recycle the clean waste water streams within the plant. ACS was also able to halve the use of sulphur based products, introduce alternative surfactants and set realistic targets for levels of TDS, BOD, COD, colour and toxicity. As a result of these initiatives, water usage has been reduced from 250 litres per kilogram of yarn to 130 litres.
ACS also introduced low temperature dyeing technology and carried out research and development work in dye bath recycling to the pilot plant stage, in conjunction with the CSIRO Division of Polymers and Chemistry. The result was that annual chemical and dye costs per kilogram of product did not change between 1992 and 1996, even though the company introduced some higher cost dyes. The company also absorbed some increases in raw material costs.
ACS has identified more than 50 individual improvement steps through the implementation of its environmental action plan and maintaining a focus on the sequence of waste reduction, recycling and reuse. This has involved the following: elimination of several waste streams; reduction in the largest process stream; removal of a range of chemical inputs from the process; and recycling of some water streams.
These improvements have also delivered significant cost savings to the company, especially through reduced trade waste charges. In addition, the contribution of these initiatives to the maintenance or improvement of product quality was a significant benefit.
Over a three year period, where dye house production increased by almost 60 per cent, the following efficiency improvements were achieved.
Parameter, per kg of product
Efficiency Improvement Achieved (%)
Water Usage
44
Chemical Usage
26
Gas Consumption
37
Power Consumption
15
Total cost
$150,000
Savings
$1,100,000 over three years
Payback
2 Months
ACS was one of three companies that discharged trade waste to the local waste water treatment plant. The quantity of effluent being discharged by the three companies was greater than the design capacity of the treatment plant. Consequently the water authority requested that contributors undertake waste audits. This provided the initial imperative for ACS to investigate cleaner production opportunities. After further discussion with the Victorian Environment Protection Authority (EPA), the company decided that it needed to focus upon the opportunities provided by cleaner production and waste minimisation in order to improve its environmental and cost performance.
The implementation of these cleaner production initiatives was based on a team oriented approach that was supported by senior management, and involved personnel from senior management through to the shop floor. The program also involved close cooperation with EPA.
The company recognised early that it was important not to lose sight of the quality aspect of its operations. It is currently applying for ISO 9002 accreditation and is implementing an environmental management system to ISO 14000 in order to achieve continuous improvement in its environmental performance.
The main barrier faced by ACS related to the development of new dyeing technology. ACS does not have its own research and development capability and is therefore reliant on cooperative programs with organisations such as the CSIRO for the development of new dyeing technology that will deliver production and environmental efficiency gains.
Case Study Prepared: January 1997 by ACCP
The Cleaner Production Case Studies Directory is part of EnviroNET Australia.
- For more information contact:
Environment Australia
Environment Protection Group
PO Box E305
KINGSTON ACT 2604
AUSTRALIA
Email: cproduction@ea.gov.au
URL: http://www.environment.gov.au/net/environet.html